Eczema
Eczema, a disease that is commonly referred to as atopic dermatitis, typically starts in early infancy and is usually genetic. It is characterized by pruritus (itchiness) xerosis (dry skin) and lichenificaiton on the skin (thickening of the skin and increase in skin markings).
Jump to
Eczema/Atopic Dermatitis
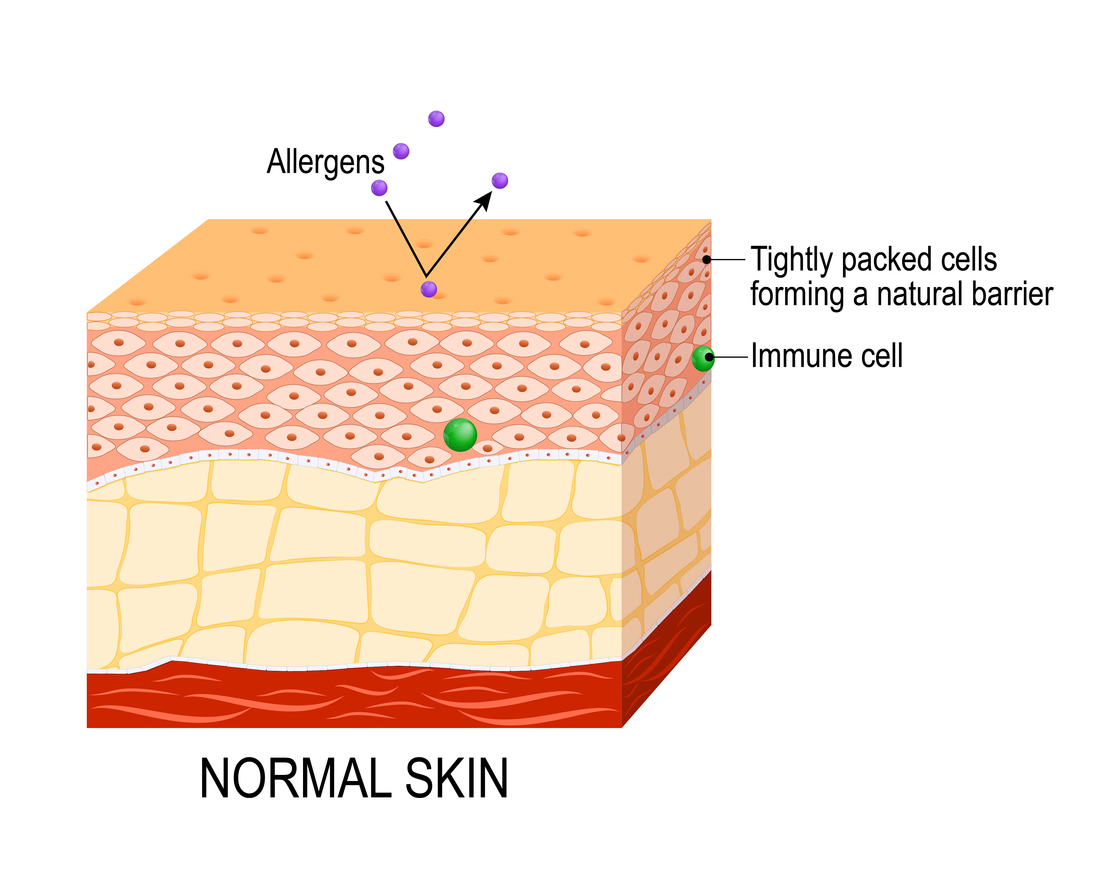
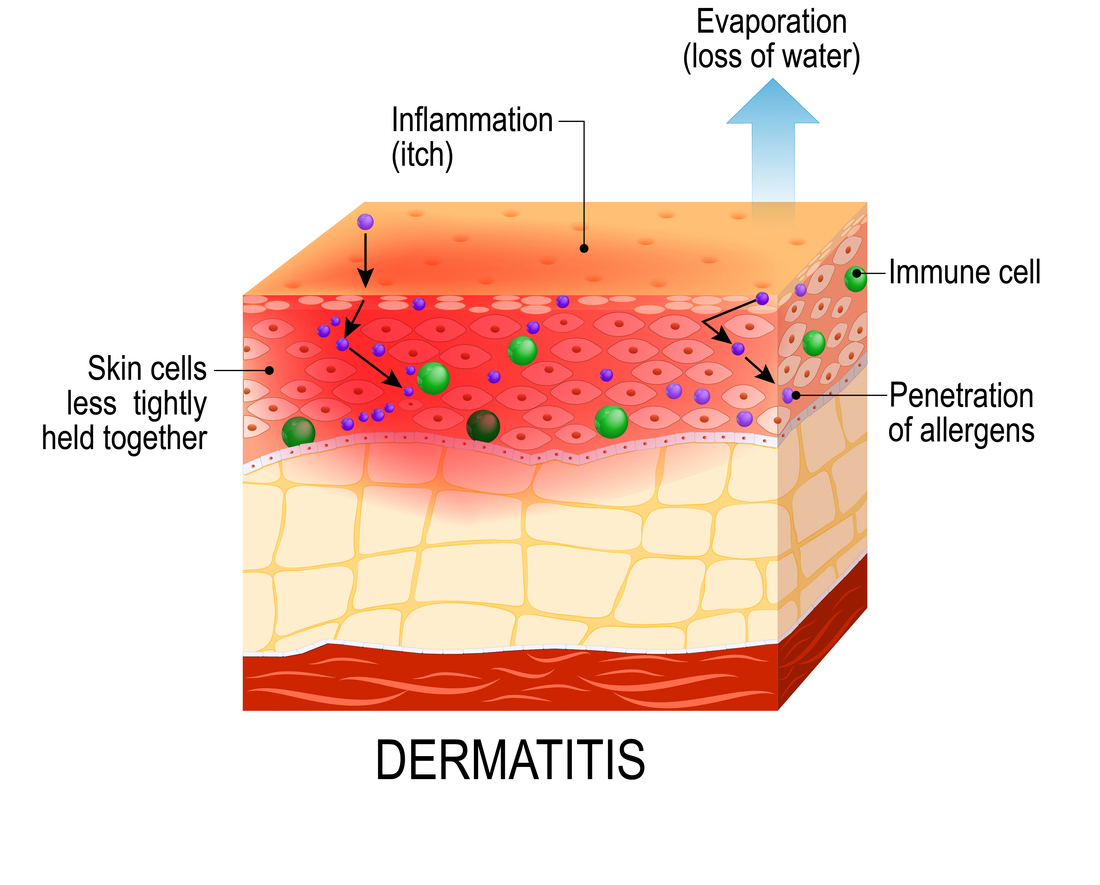
Atopic dermatitis (atopic eczema). Healthy skin and cross-section of human skin with dermatitis, showing changes and differences.
Types
& Causes
Eczema
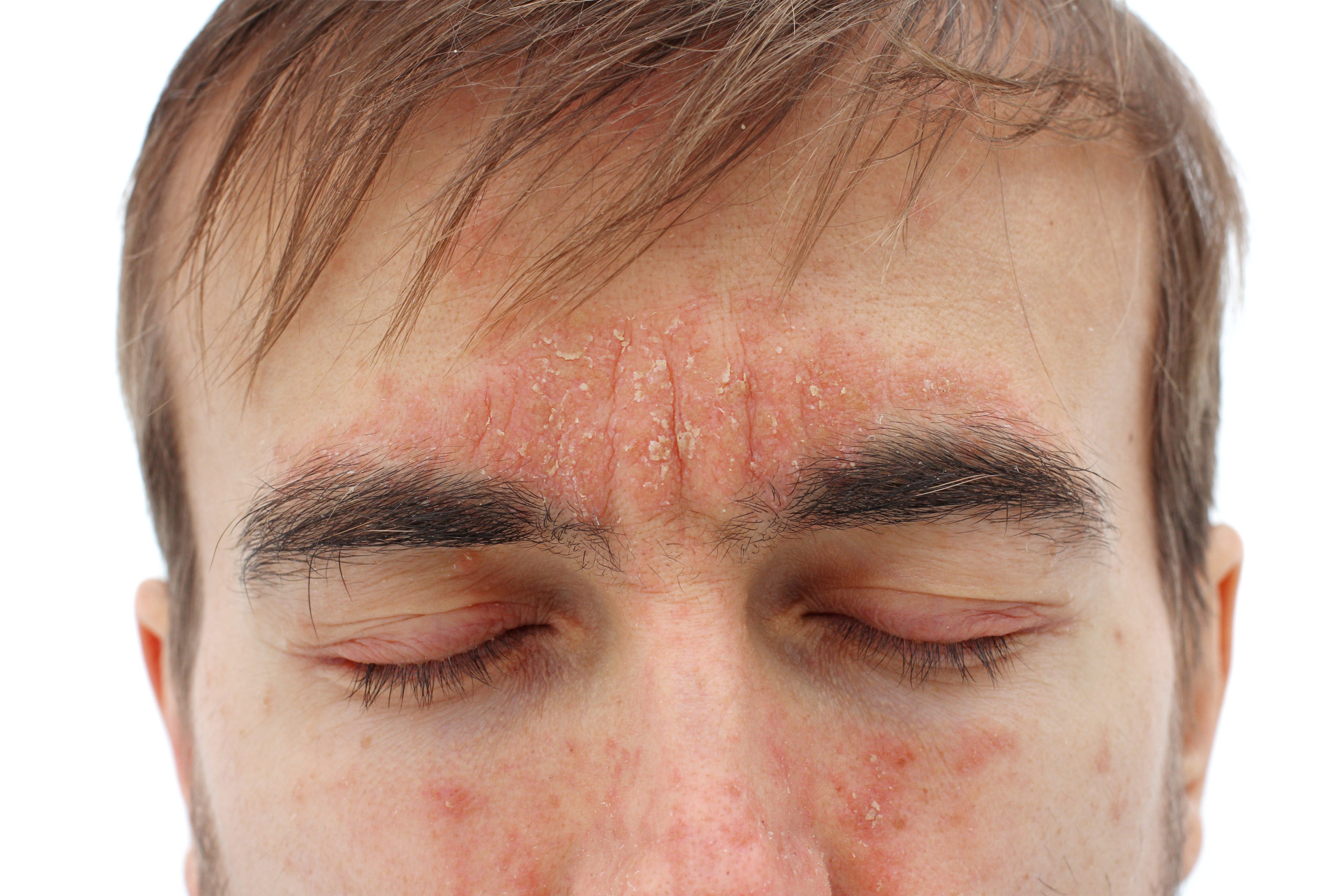
Symptoms
Common symptoms for all types of eczema:
- dry, scaly skin
- redness
- itching, which may be intense
- personal history of allergies
- sensitivity to allergens, such as dust mites, pollen, animal dander, and molds
- food allergies, including cow’s milk, eggs, peanuts, and soy
- history of asthma or hay fever
- commonly occurs in three stages and may lie dormant between each stage (infancy, childhood, adulthood)
Hand Eczema

Eczema that only affects your hands is called hand eczema. You may get this type if you work in a job like hairdressing or cleaning, where you regularly use chemicals that irritate the skin.
Symptoms
In hand eczema:
- your hands get red, itchy, and dry
- they may form cracks or blisters
Contact Dermatitis
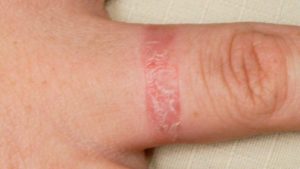
Contact dermatitis on the hand from a metal ring.
If you have red, irritated skin that’s caused by a reaction to substances you touch, you may have contact dermatitis. It comes in two types: Allergic contact dermatitis, an immune system reaction to an irritant like latex or metal. Irritant contact dermatitis starts when a chemical or other substance irritates your skin. Some common culprits include cosmetics, fragrances, and jewelry.
Symptoms
In contact dermatitis:
- your skin itches, turns red, burns, and stings
- itchy bumps called hives may pop up on your skin
- fluid-filled blisters can form that may ooze and crust over
- over time, the skin may thicken and feel scaly or leathery
Treatments
& Protocols
How to Treat
-
Sensitive Skin: Gently Exfoliate and Increase Cell Turnover -
Sensitive Skin: Decrease Redness and Inflammation -
Sensitive Skin: Increase Hydration to Control Excessive Dryness -
Sensitive Skin: Protect from UV Exposure (SPF)
Professional Treatment Protocols
-
Hydrate: Therapeutic Oat Milk Mask for Sensitized Skin Conditions -
Aggravated Atopic Dermatitis/Eczema Treatment -
Non-Inflamed Atopic Dermatitis/Eczema Treatment

